
Slide navigation: Forward with space bar, → arrow key, or PgDn. Backwards with ← or PgUp.
public class DayTest
{
@Test public void testAdd() { . . . }
@Test public void testDaysBetween() { . . . }
. . .
}java -classpath .:pathToJUnit/\* org.junit.runner.JUnitCore DayTest
main method is in org.junit.runner.JUnitCore@Test annotationspublic abstract class TestCase
{
public abstract void execute() throws Exception;
...
}execute for each test case: TestCase[] testCases = ...;
for (TestCase t : testCases)
{
try
{
t.execute();
Report success
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Report failure
}
}
public abstract class TestCase
{
. . .
public void assertEquals(Object expected, Object actual)
{
if (!Objects.equals(actual, expected))
throw new TestException("Expected: " + expected + ", Actual: " + actual);
}
}public abstract class TestSuite
{
public abstract TestCase[] getTestCases();
public List<TestResult> run() { ... }
}import java.util.List;
public class TestRunner
{
public static void main(String[] args)
throws ReflectiveOperationException
{
for (String arg : args)
{
Class<?> testSuiteClass = Class.forName(arg);
TestSuite suite = (TestSuite) testSuiteClass.newInstance();
List<TestResult> results = suite.run();
for (TestResult result : results)
System.out.println(result);
}
}
}public class TestAdd implements TestCase
{
public void execute()
{
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i = i * 100)
{
Day d1 = new Day(1970, 1, 1);
Day d2 = d1.addDays(i);
assertEquals(i, d2.daysFrom(d1));
}
}
}public class DayTestSuite extends TestSuite
{
public TestCase[] getTestCases()
{
return new TestCase[] { new TestAdd(), new TestAddNegative(), ... }
}
}java TestRunner DayTestSuite
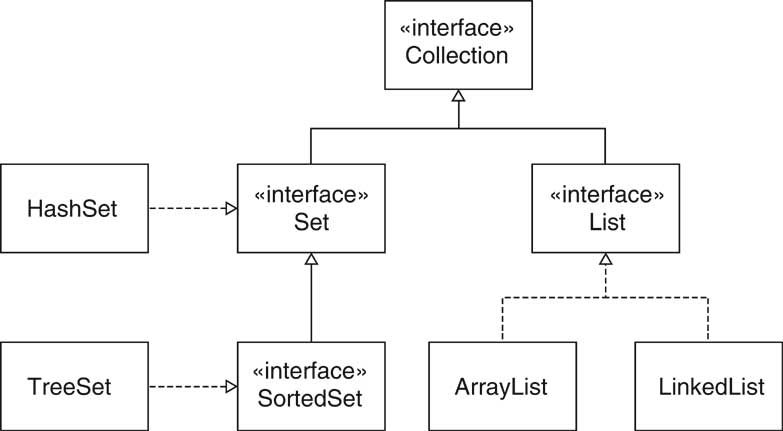
HashSet: a set implementation that uses hashing to locate the set elements
TreeSet: a sorted set implementation that stores the elements in a balanced binary tree
LinkedList and ArrayList: two implementations of the List interface type
Collection<E> Interface Type
boolean add(E obj) boolean addAll(Collection c) void clear() boolean contains(E obj) boolean containsAll(Collection c) boolean equals(E obj) int hashCode() boolean isEmpty() Iterator iterator() boolean remove(E obj) boolean removeAll(Collection c) boolean retainAll(Collection c) int size() E[] toArray() E[] toArray(E[] a)
Iterator<E> Interface Type
boolean hasNext() E next() void remove()
AbstractCollection ClassCollection is a hefty interface toArray
public E[] toArray()
{
E[] result = new E[size()];
Iterator e = iterator();
for (int i = 0; e.hasNext(); i++)
result[i] = e.next();
return result;
}
AbstractCollection ClassAbstractCollection class
AbstractCollection convenient superclass for implementors size,iterator
remove method) add method always returns true 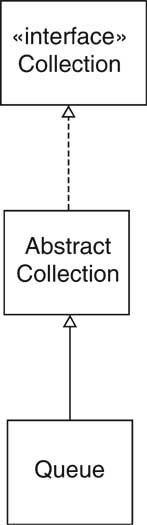
Set interface adds no methods to Collection! Set boolean add(int index, E obj) boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) E get(int index) int indexOf(E obj) int lastIndexOf(E obj) ListIterator listIterator() ListIterator listIterator(int index) E remove(int index) E set(int index, int E) List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
int nextIndex() int previousIndex() boolean hasPrevious() E previous() void set(E obj)
ArrayList LinkedList RandomAccess interface 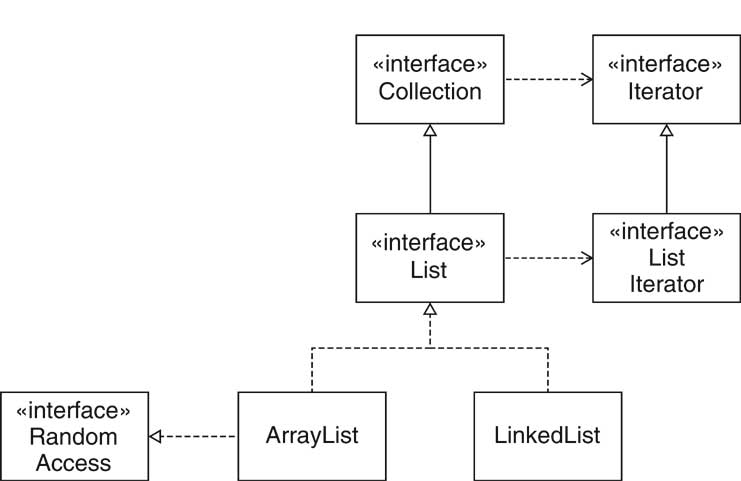
Collection.add, Collection.remove Arrays.asList
String[] strings = { "Kenya", "Thailand", "Portugal" };
List view = Arrays.asList(strings) otherList.addAll(view); get/set are defined to access underlying array Arrays.asList view has no add/remove operations 
"Transistor") Class objects? (Transistor.class) Node, Edge objects? (new Transistor()) new CircleNode(Color.BLACK) new CircleNode(Color.WHITE)
Node prototype = node of currently selected toolbar button; Node newNode = (Node) prototype.clone(); Point2D mousePoint = current mouse position; graph.add(newNode, mousePoint);
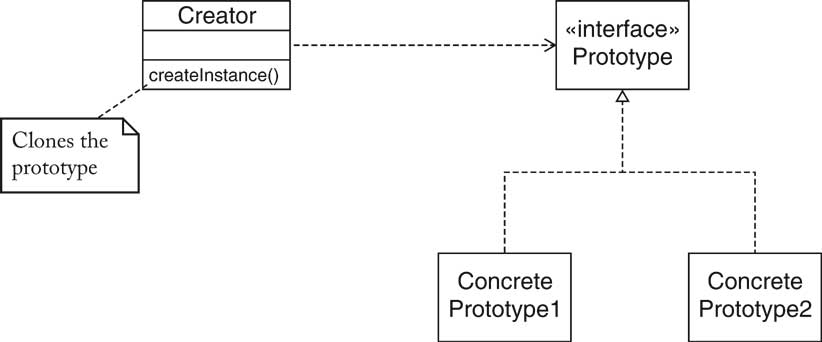
| Name in Design Pattern | Actual name (graph editor) |
|---|---|
Prototype
|
Node
|
ConcretePrototype1
|
CircleNode
|
Creator
|
The GraphPanel that handles the mouse operation for adding new nodes
|
Node/Edge interfaces draw draws node/edge getBounds returns enclosing rectangle (to compute total graph size for scrolling) Edge.getStart, getEnd yield start/end nodes Node.getConnectionPoint computes attachment point on shape boundary Edge.getConnectionPoints yields start/end coordinates (for grabbers) clone overridden to be public 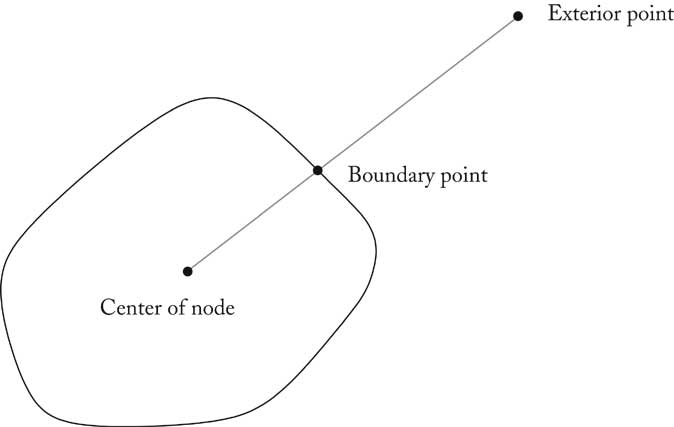
AbstractEdge class for convenience Node/Edge type or extends AbstractEdge
Graph collects nodes and edges public abstract Node[] getNodePrototypes()public abstract Edge[] getEdgePrototypes()
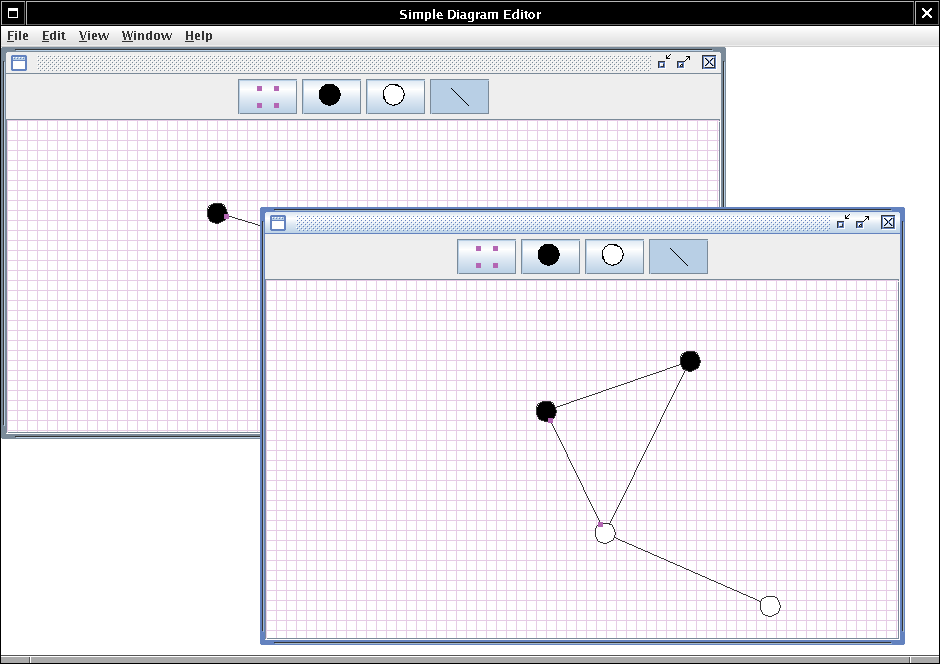
GraphFrame: a frame that manages the toolbar, the menu bar, and the graph panel.
ToolBar: a panel that holds toggle buttons for the node and edge icons.
GraphPanel: a panel that shows the graph and handles the mouse clicks and drags for the editing commands.
Node or Edge interface type Graph class and supply getNodePrototypes, getEdgePrototypes
main method 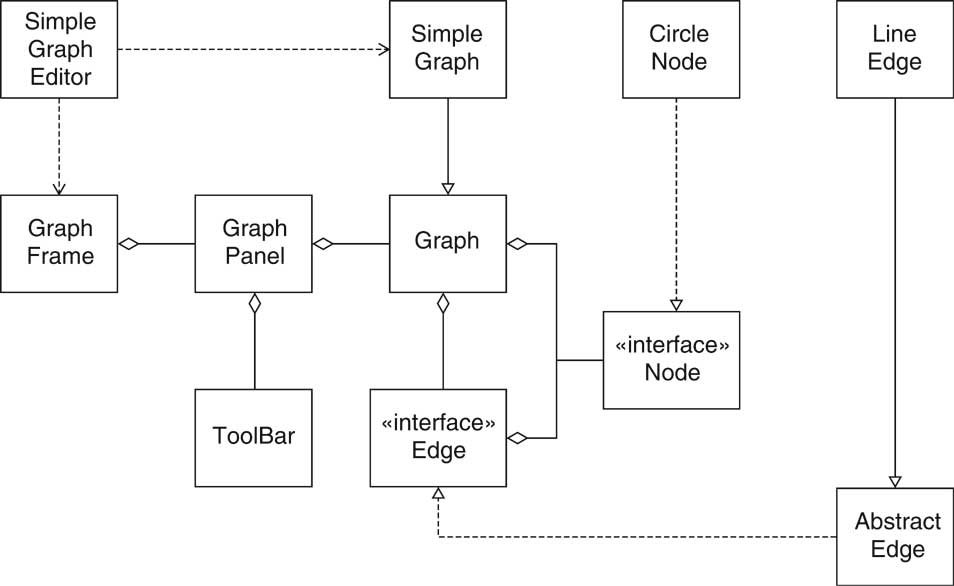
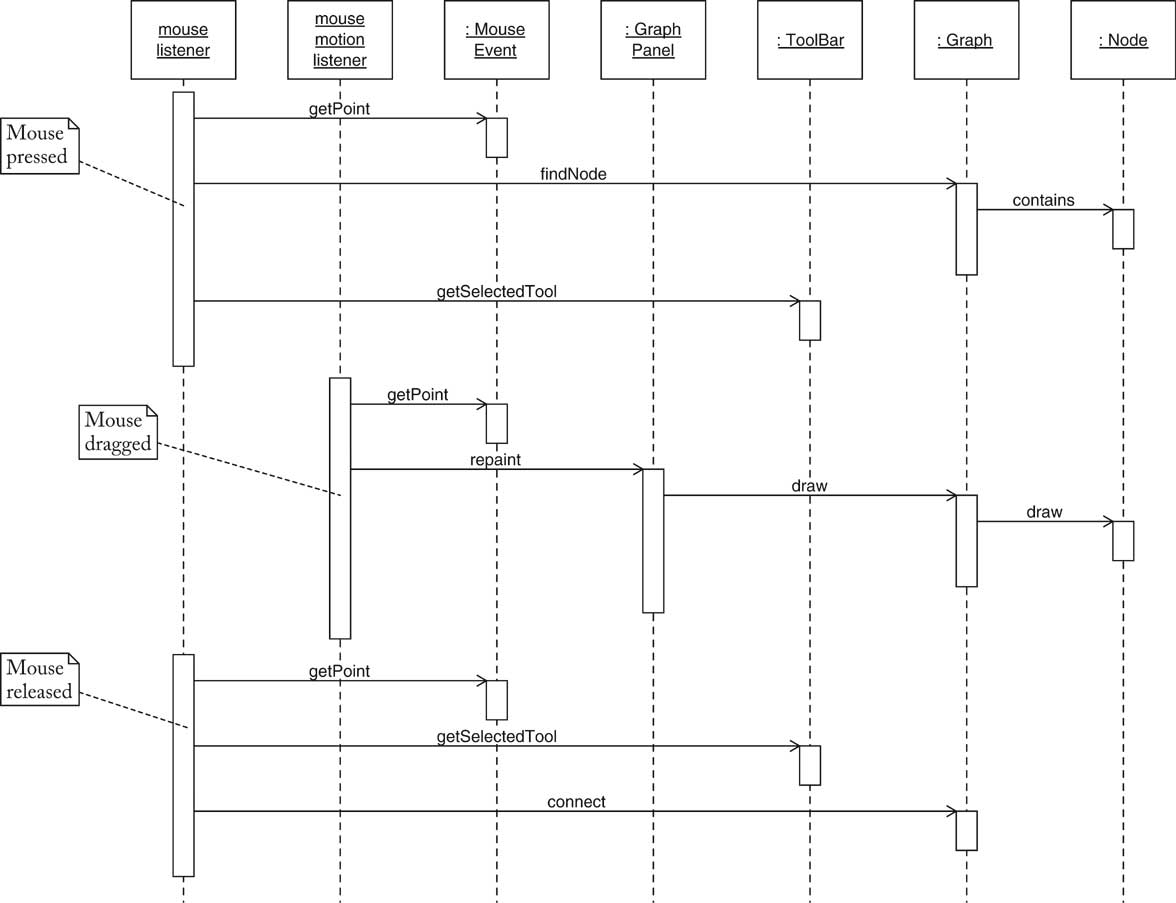
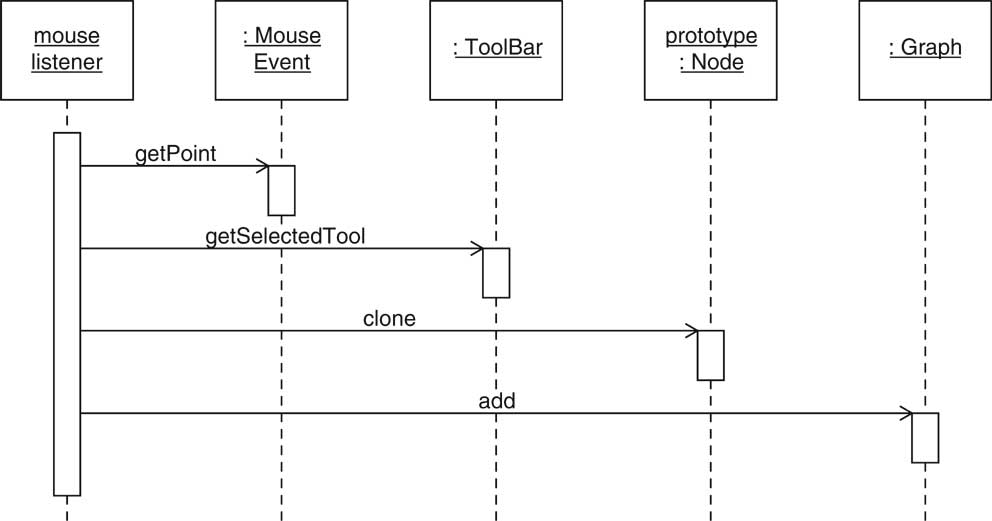
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent event)
{
Point2D mousePoint = event.getPoint();
Object tool = toolBar.getSelectedTool();
...
if (tool instanceof Node)
{
Node prototype = (Node) tool;
Node newNode = (Node)prototype.clone();
graph.add(newNode, mousePoint);
}
...
repaint();
}
public Node findNode(Point2D p)
{
for (int i = 0; i < nodes.size(); i++)
{
Node n = (Node) nodes.get(i);
if (n.contains(p)) return n;
}
return null;
}
mousePressed:
mouseDragged:
mouseReleased:

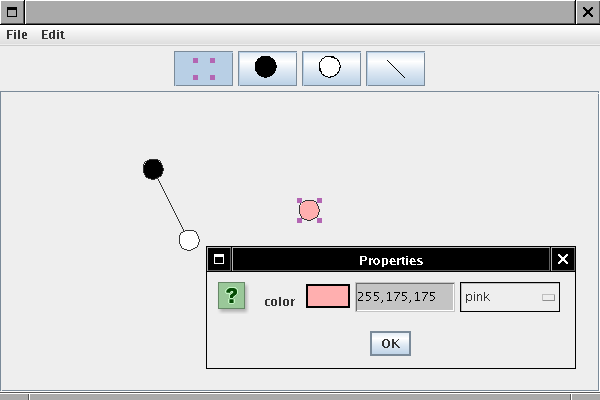
CircleNode exposes color property:
Color getColor()
void setColor(Color newValue) LineStyle
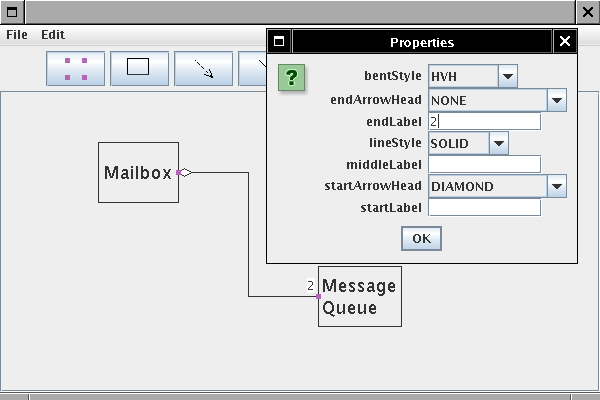
LineStyle.SOLID, LineStyle.DOTTED lineStyle property to LineEdge
LineStyle has method getStroke() LineEdge.draw calls getStroke() LineStyle type 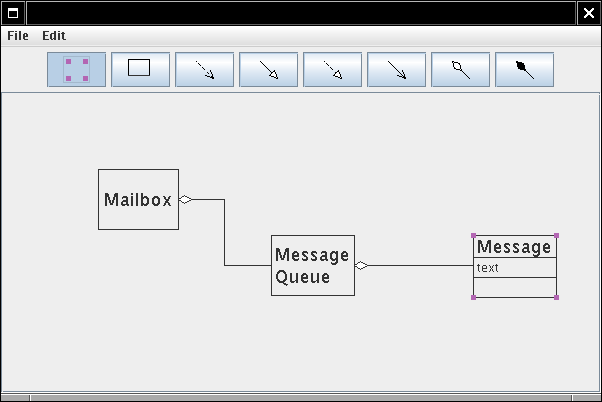
RectangularNode SegmentedLineEdge GeneralPathEdge uses general path for containment testing ArrowHead, BentStyle enumerate arrow and line styles MultiLineString property for class compartments ClassNode, ClassRelationshipEdge, ClassDiagramGraph