


1, -4, 0
0.5, -3.11111, 4.3E24, 1E-14
int n = 1000000; System.out.println(n * n); // prints -727379968
| Type | Description | Size |
|---|---|---|
| int | The integer type, with range -2,147,483,648 (Integer.MIN_VALUE) . . . 2,147,483,647 (Integer.MAX_VALUE) | 4 bytes |
| byte | The type describing a single byte, with range -128 . . . 127 | 1 byte |
| short | The short integer type, with range -32768 . . . 32767 | 2 bytes |
| long | The long integer type, with range -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 . . . 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 | 8 bytes |
| double | The double-precision floating-point type, with a range of about ±10308 and about 15 significant decimal digits | 8 bytes |
| float | The single-precision floating-point type, with a range of about ±1038 and about 7 significant decimal digits | 4 bytes |
| char | The character type, representing code units in the Unicode encoding scheme | 2 bytes |
| boolean | The type with the two truth values false and true | 1 bit |
double f = 4.35; System.out.println(100 * f); // prints 434.99999999999994
double balance = 13.75; int dollars = balance; // Error
Suppose you want to write a program that works with population data from various countries. Roughly half of the world population lives in India and China, each of which has about 1.2 x 109 inhabitants.
Which of the below is the best argument for selecting an appropriate Java data type?
int because a country never has a fractional number of
peopleint because it is more accurate than
doubledouble because an int cannot hold a number
as large as 1.2 x 109 double because an int cannot hold the
entire world populationfinal double QUARTER_VALUE = 0.25; final double DIME_VALUE = 0.1; final double NICKEL_VALUE = 0.05; final double PENNY_VALUE = 0.01; payment = dollars + quarters * QUARTER_VALUE + dimes * DIME_VALUE + nickels * NICKEL_VALUE + pennies * PENNY_VALUE;
public class Math
{
. . .
public static final double E = 2.7182818284590452354;
public static final double PI = 3.14159265358979323846;
}
double circumference = Math.PI * diameter;

/**
A cash register totals up sales and computes change due.
*/
public class CashRegister
{
public static final double QUARTER_VALUE = 0.25;
public static final double DIME_VALUE = 0.1;
public static final double NICKEL_VALUE = 0.05;
public static final double PENNY_VALUE = 0.01;
private double purchase;
private double payment;
/**
Constructs a cash register with no money in it.
*/
public CashRegister()
{
purchase = 0;
payment = 0;
}
/**
Records the purchase price of an item.
@param amount the price of the purchased item
*/
public void recordPurchase(double amount)
{
purchase = purchase + amount;
}
/**
Enters the payment received from the customer.
@param dollars the number of dollars in the payment
@param quarters the number of quarters in the payment
@param dimes the number of dimes in the payment
@param nickels the number of nickels in the payment
@param pennies the number of pennies in the payment
*/
public void enterPayment(int dollars, int quarters,
int dimes, int nickels, int pennies)
{
payment = dollars + quarters * QUARTER_VALUE + dimes * DIME_VALUE
+ nickels * NICKEL_VALUE + pennies * PENNY_VALUE;
}
/**
Computes the change due and resets the machine for the next customer.
@return the change due to the customer
*/
public double giveChange()
{
double change = payment - purchase;
purchase = 0;
payment = 0;
return change;
}
}
/**
This class tests the CashRegister class.
*/
public class CashRegisterTester
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
CashRegister register = new CashRegister();
register.recordPurchase(0.75);
register.recordPurchase(1.50);
register.enterPayment(2, 0, 5, 0, 0);
System.out.print("Change: ");
System.out.println(register.giveChange());
System.out.println("Expected: 0.25");
register.recordPurchase(2.25);
register.recordPurchase(19.25);
register.enterPayment(23, 2, 0, 0, 0);
System.out.print("Change: ");
System.out.println(register.giveChange());
System.out.println("Expected: 2.0");
}
}
Program Run:
Change: 0.25 Expected: 0.25 Change: 2.0 Expected: 2.0
What is wrong with the following statement sequence?
double radius = 20; double circumference = 3.14 * radius;
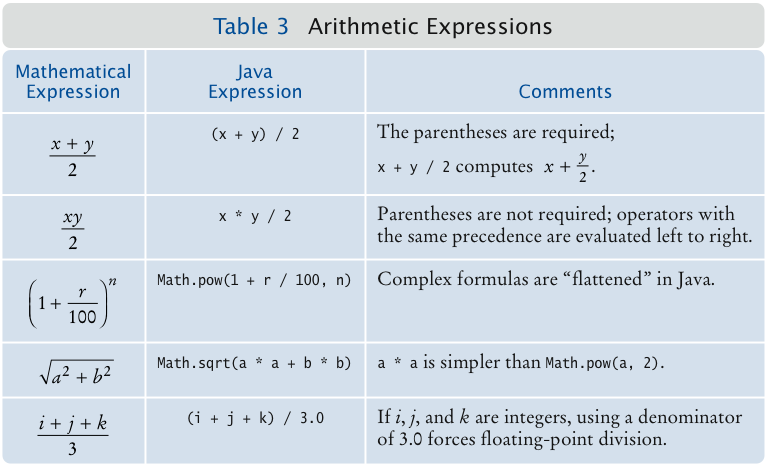
(a + b) / 2
a + b / 2
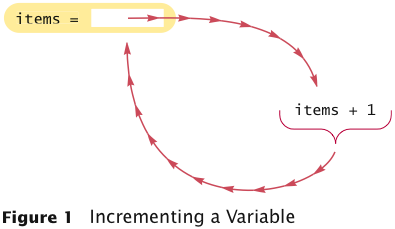
Example:
final int PENNIES_PER_NICKEL = 5; final int PENNIES_PER_DIME = 10; final int PENNIES_PER_QUARTER = 25; final int PENNIES_PER_DOLLAR = 100; // Compute total value in pennies int total = dollars * PENNIES_PER_DOLLAR + quarters * PENNIES_PER_QUARTER + nickels * PENNIES_PER_NICKEL + dimes * PENNIES_PER_DIME + pennies; // Use integer division to convert to dollars, cents int dollars = total / PENNIES_PER_DOLLAR; int cents = total % PENNIES_PER_DOLLAR;
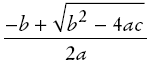

| Function | Returns |
|---|---|
| Math.sqrt(x) | square root |
| Math.pow(x, y) | power xy |
| Math.exp(x) | ex |
| Math.log(x) | natural log |
| Math.sin(x), Math.cos(x), Math.tan(x) | sine, cosine, tangent (x in radians) |
| Math.round(x) | closest integer to x |
| Math.min(x, y), Math.max(x, y) | minimum, maximum |
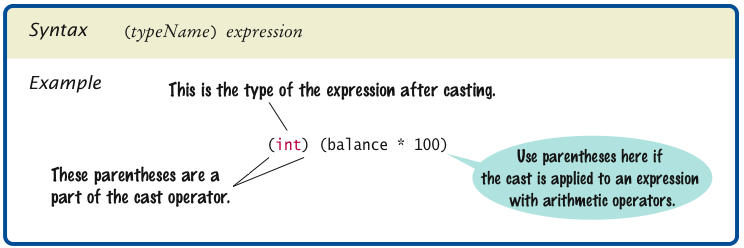
double balance = total + tax; int dollars = (int) balance;
Cast discards fractional part.
long rounded = Math.round(balance); // if balance is 13.75, then
// rounded is set to 14
What is the value of n after the following sequence of statements?
int n = 10; n++; n = n % 10; n--; n--;
The variable price contains the price of a product in dollars
and cents, such as 19.75. You want to get the dollars. What do you
do?
int dollars = (int) Math.round(price);int dollars = (int) price;int dollars = price / 100;int price = ((int) price * 100) / 100;