CS 46A - Lecture 4

Pre-class reading

- Sections 2.4 - 2.6
- Did you take the quiz?
Objects and Classes
- Object: entity that you can manipulate in your programs
by calling methods
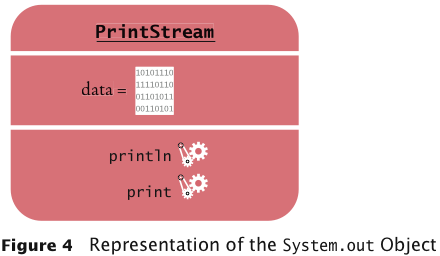
- Each object belongs to a class. For example,
System.out belongs to the class PrintStream
Methods
A Representation of Two String Objects
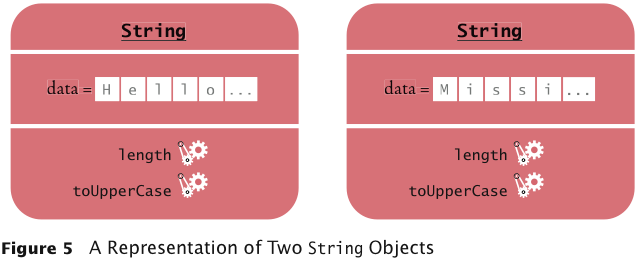
String Methods
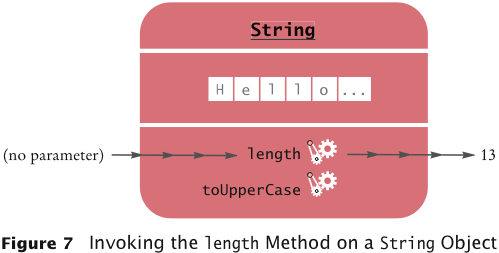
- length: counts the number of characters in a string:
String greeting = "Hello, World!";
int n = greeting.length(); // sets n to 13
- toUpperCase: creates another String object that
contains the characters of the original string, with lowercase letters
converted to uppercase:
String river = "Mississippi";
String bigRiver = river.toUpperCase(); // sets bigRiver to "MISSISSIPPI"
- When applying a method to an object, make sure method is defined in the
appropriate class:
System.out.length(); // This method call is an error
Lecture 4 Clicker Question 1
What does the following program segment print?
String name = "Fred";
System.out.print(name);
System.out.println("name".toUpperCase());
- Nothing—the code contains a compile-time error
FredNAME
FredFRED
Fred
FRED
Lecture 4 Clicker Question 2
What does the following program segment print?
String name = "Fred";
name.println();
int length = name.length();
length.println();
- Nothing—the code contains a compile-time error
Fred4
Fred
4
FRED
4
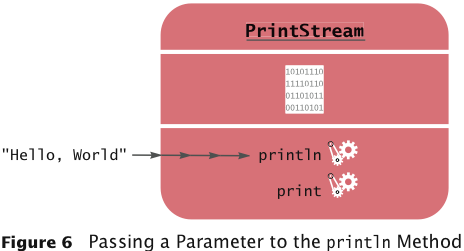
Parameters
- Parameter: an input to a method
- Implicit parameter: the object on which a method is
invoked:
System.out.println(greeting)
- Explicit parameters: all parameters except the implicit
parameter:
System.out.println(greeting)
- Not all methods have explicit parameters:
greeting.length() // has no explicit parameter
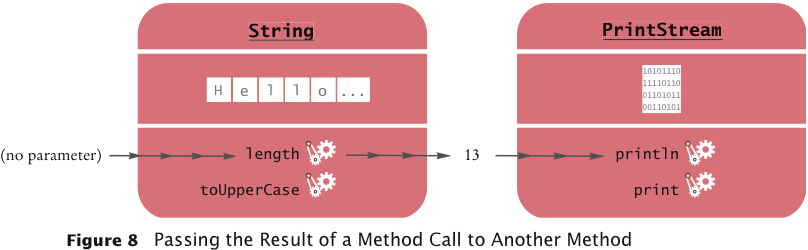
Return Values
Passing Return Values
A More Complex Call
Lecture 4 Clicker Question 3
What is true about the method call river.length()?
- It has one implicit parameter, no explicit parameter, and no return
value
- It has one implicit parameter, no explicit parameter, and one return
value
- It has no implicit parameter, one explicit parameter, and no return
value
- It has no implicit parameter, one explicit parameter, and oe return
value
Lecture 4 Clicker Question 4
What does the following program segment print?
String name = "Fred";
PrintStream out = System.out;
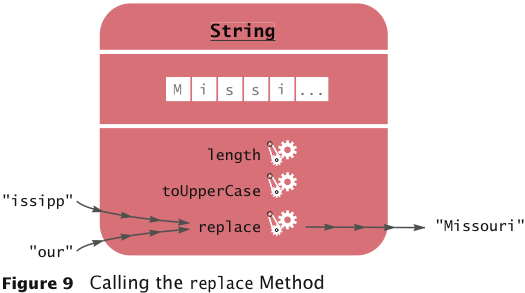
out.println(name.replace("r", "e").replace("e", "o").toLowerCase());
- Nothing—the code contains a compile-time error
frrd
food
4
Rectangular Shapes and Rectangle Objects
- Objects of type Rectangle describe rectangular shapes:
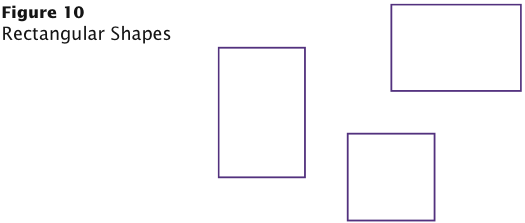
Rectangular Shapes and Rectangle Objects
- A Rectangle object isn't a rectangular shape — it is an object
that contains a set of numbers that describe the rectangle:
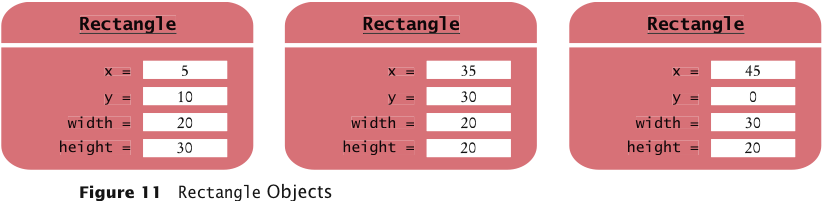
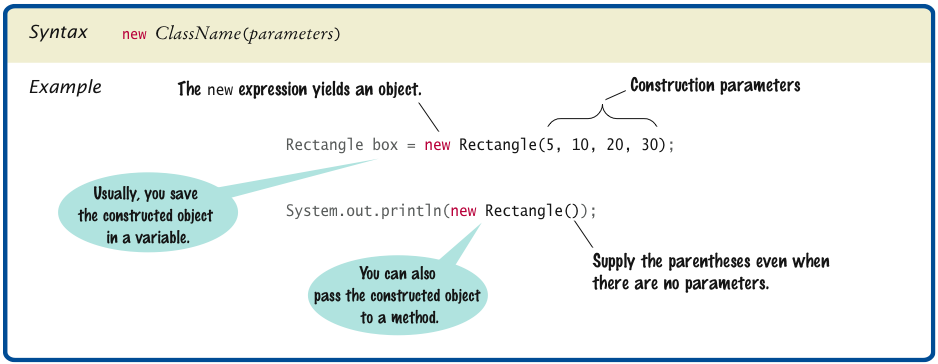
Constructing Objects
new Rectangle(5, 10, 20, 30)
Constructing Objects
- Construction: the process of creating a new object
- The four values 5, 10, 20, and 30 are
called the construction parameters
- Some classes let you construct objects in multiple ways:
new Rectangle()
// constructs a rectangle with its top-left corner
// at the origin (0, 0), width 0, and height 0
Syntax 2.3 Object
Construction
Lecture 4 Clicker Question 5
What does the following program segment print?
Rectangle rect = new Rectangle(10, 10, 10, 10);
PrintStream out = System.out;
out.println(rect.length());
- Nothing—the code contains a compile-time error
10
20
40