
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 United States License.
Copyright © Cay S. Horstmann 2009 
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 United States License.
Part A: Simple array algorithms
oddCount and evenCount), what is the Java code
for returning them together in an array? Part B. Removing duplicates
ArrayList<String> called
words. Your task is to add a method
removeAdjacentDuplicates that removes all adjacent duplicates
in words. Develop a plan and write pseudocode for this task.
How will you find duplicates? What will you do when you find them? Pay
special attention to what happens at the beginning or end of the array
list. Make a Text object on the BlueJ workbench. Right-click and
call pick. Pick the file typo.txt. Right-click and call
removeAdjacentDuplicates (i.e. your method). Right-click and
call explore. Is the duplicate “be” removed?
Mary had a little lamb little lamb little lamb Mary had a little lamb whose fleece was white as snow And everywhere that Mary went Mary went Mary went And everywhere that Mary went the lamb was sure to go
you should produce the array list
Mary had a little lamb whose fleece was white as snow And everywhere that went the was sure to go
Decide upon an algorithm and write down the pseudocode.
Ask yourselves:
removeAllDuplicates to the Text class. Provide
your implementation and test it as described above.Part C. Swapping
swapNeighbors
method is intended to swap neighboring elements. For example,
1 4 9 16 25 36
is supposed to turn int
4 1 16 9 36 25
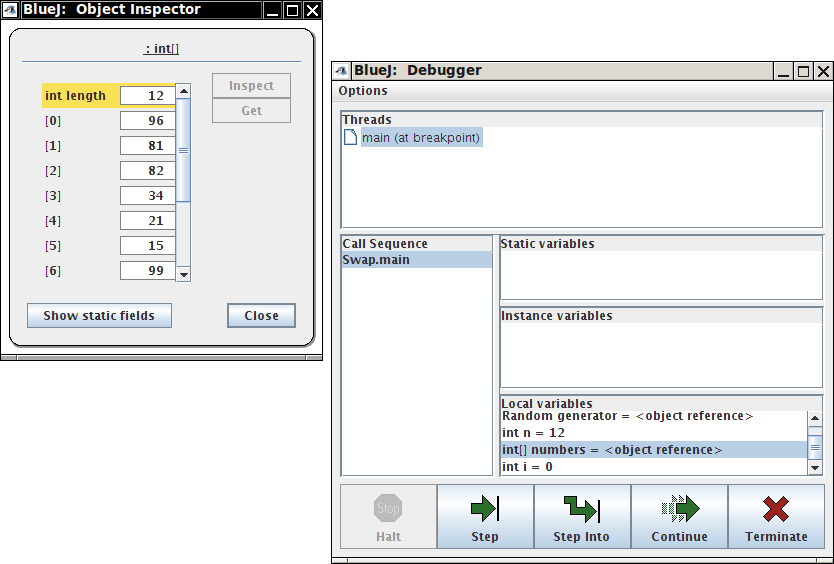
But as you can see, it doesn't work. Now launch the BlueJ debugger. Step
into the swapNeighbors method. Then keep clicking
Step and observe the program behavior until you can tell
why it fails to swap the values.
Tip: To see the contents of the array, double-click on it in the Local Variables pane.
Part D. More Swapping with Alice
myFirstMethod method in the
Scene class. Note that a VisualArrayList is
exactly like an ArrayList, except it shows you in slow motion
what goes on inside.
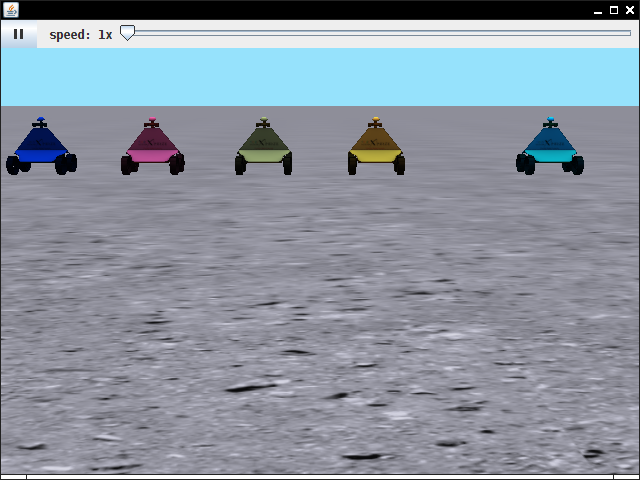
For example, A B C D E F should turn into D E F A B
C.
You should assume that the array list has an even number of elements (not necessarily 6).
One solution is to keep removing the element at index 0 and adding it to the back.
A B C D E F B C D E F A C D E F A B D E F A B C
Write pseudocode for this algorithm.
Ask yourselves:
run method
into your lab report.remove(0) causes n - 1
elements to move, where n is the length of the array. If
n is 100, then you move 99 elements 50 times, (almost 5000 move
operations). That's an inefficient way of swapping the first and second
halves.
Come up with a better way in which you swap the elements directly.
A B C D E F D B C A E F D E C A B F D E F A B C
Write pseudocode for this algorithm.
Ask yourselves:
run method
into your lab report. Watch how much faster it runs. (In Alice, this is
pretty obvious since the movement of the array elements takes time.)
Set NCARS to 10 and run the program again to double-check
that it works with any even number of cars.
Part E. 2D arrays
makePattern method fills a two-dimensional array
colors[15][10] with colors. 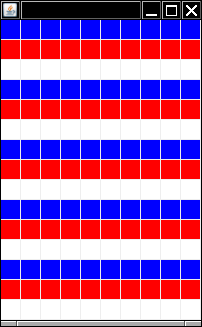
Ask yourselves:
makePattern method in your lab report.