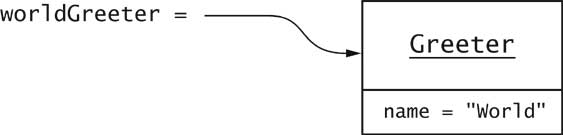
Greeter worldGreeter = new Greeter("World");
Greeter anotherGreeter = worldGreeter;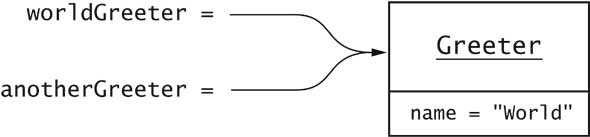
anotherGreeter.setName("Dave");
// now worldGreeter.sayHello() returns "Hello, Dave!"

Slide navigation: Forward with space bar, → arrow key, or PgDn. Backwards with ← or PgUp.
Greeter(String aName) sayHello() namepublic or private new operatornew Greeter("World")
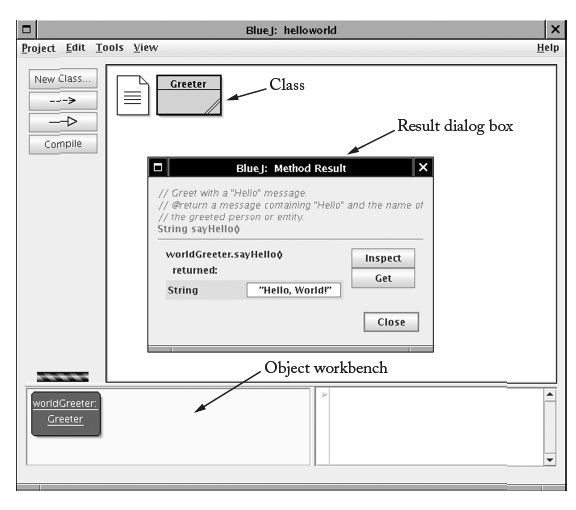
new Greeter("World").sayHello()
Greeter worldGreeter = new Greeter("World");
String greeting = worldGreeter.sayHello();
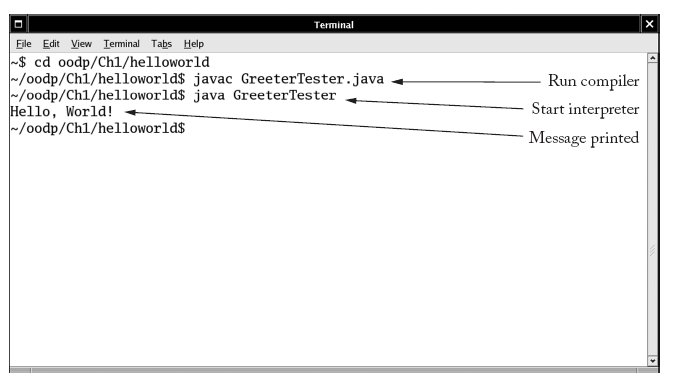
main method is called when program starts main is static: it doesn't operate on any objects main starts main constructs objects and invokes methodscd to directory that holds your files javac GreeterTest.javaNote that Greeter.java is automatically compiled.
java GreeterTest
/** ... */ @param parameter explanation @return explanation 
int, long, short, byte double, float
char boolean 'a', '\n', '\x2122' (int) x, (float) x Math class has methods that operate on numbers:y = Math.sqrt(x);
if while do/while for for loop:for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
. . .
}
// i no longer defined here
Greeter worldGreeter = new Greeter("World");

Greeter anotherGreeter = worldGreeter;
anotherGreeter.setName("Dave");
// now worldGreeter.sayHello() returns "Hello, Dave!"
null Referencenull refers to no object null to object variable:
worldGreeter = null;
null
if (worldGreeter == null) . . .
null causes NullPointerException this Reference
public boolean equals(Greeter other)
{
if (this == other) return true;
return name.equals(other.name);
}
public Greeter(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public void copyNameTo(Greeter other)
{
other.name = this.name;
}
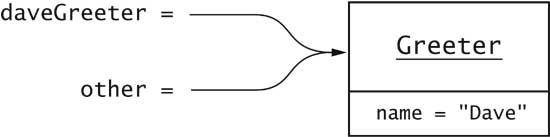
Greeter worldGreeter = new Greeter("World");
Greeter daveGreeter = new Greeter("Dave");
worldGreeter.copyNameTo(daveGreeter);
public void copyLengthTo(int n)
{
n = name.length();
}
public void copyGreeterTo(Greeter other)
{
other = new Greeter(name);
}
int length = 0; worldGreeter.copyLengthTo(length); // length still 0 worldGreeter.copyGreeterTo(daveGreeter) // daveGreeter unchanged
java.util javax.swing com.sun.misc edu.sjsu.cs.cs151.alice
package statement to top of file
package edu.sjsu.cs.cs151.alice;
public class Greeter { . . . }
java.util.ArrayList javax.swing.JOptionPane
import allows you to use short class name
import java.util.Scanner; . . . Scanner a; // i.e. java.util.Scanner
import java.util.*;
import java.*.*; // NO
import is no help.
import java.util.*; import java.sql.*; . . . java.util.Date d; // Date also occurs in java.sql
java.lang.
edu.sjsu.cs.sjsu.cs151.alice.Greetermust be in subdirectory
basedirectory/edu/sjsu/cs/sjsu/cs151/alice
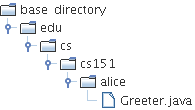
javac edu/sjsu/cs/sjsu/cs151/alice/Greeter.javaor
javac edu\sjsu\cs\sjsu\cs151\alice\Greeter.java
java edu.sjsu.cs.cs151.alice.GreeterTest
NullPointerException
String name = null; int n = name.length(); // ERROR
null Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException at Greeter.sayHello(Greeter.java:25) at GreeterTest.main(GreeterTest.java:6)
NullPointerException is not checked IOException is checked FileNotFoundException:
public void write(String filename) throws FileNotFoundException
{
PrintWriter reader = new PrintWriter(filename, "UTF-8");
. . .
}
public void read(String filename)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
try
{
code that might throw an IOException
}
catch (IOException exception)
{
take corrective action
}
exception.printStackTrace(); System.exit(1);
try-with-Resourcestry block
try (PrintWriter writer = new PrintWriter(filename, "UTF-8"))
{
. . .
}close method called
try block exits normallytry blockAutoCloseablefinally Clauseclose, use try-with-resourcesfinally clausetry
{
...
}
finally
{
lock.unlock();
}
unlock method called
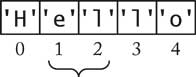
try block exits normallytry blocklength method yields number of char values "" is the empty string of length 0, different from null charAt method yields char values:
char c = s.charAt(i); substring method yields substrings:
"Hello".substring(1, 3) is "el"
equals to compare strings
if (greeting.equals("Hello")) == only tests whether the object references are identical:
if ("Hello".substring(1, 3) == "el") ... // NO! + operator concatenates strings:
"Hello, " + name
+ is a string, the other is converted into a string:
int n = 7; String greeting = "Hello, " + n; // yields "Hello, 7"
toString method is applied to objects
Date now = new Date(); String greeting = "Hello, " + now; // concatenates now.toString() // yields "Hello, Wed Jan 17 16:57:18 PST 2001"
Integer.parseInt
Double.parseDouble String input = "7"; int n = Integer.parseInt(input); // yields integer 7
NumberFormatException (unchecked) Scanner from input stream (e.g. System.in)
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in)
nextInt, nextDouble reads next int or double
int n = in.nextInt();
hasNextInt, hasNextDouble test whether next token is a number next reads next string (delimited by whitespace) nextLine reads next line
ArrayList<E> classArrayList<E> collects objects of type E E
add appends to the end
ArrayList<String> countries = new ArrayList<>();
countries.add("Belgium");
countries.add("Italy");
countries.add("Thailand");
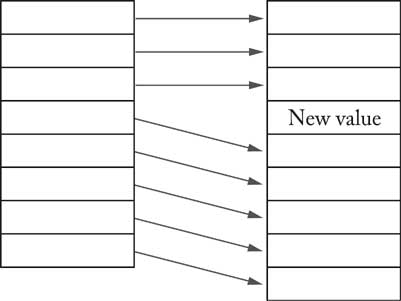
ArrayList<E> classget gets an element; no need to cast to correct type:
String country = countries.get(i); setcountries.set(1, "France"); size method yields number of elements
for (int i = 0; i < countries.size(); i++) . . . for (String country : countries) . . .
ArrayList<E> class
countries.add(1, "Germany");
countries.remove(0);
add appends to the end
LinkedList<String> countries = new LinkedList<>();
countries.add("Belgium");
countries.add("Italy");
countries.add("Thailand");
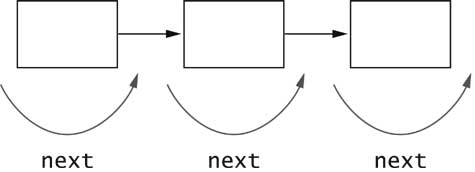
next
ListIterator<String> iterator = countries.listIterator();
while (iterator.hasNext())
{
String country = iterator.next();
. . .
} for (String country : countries)
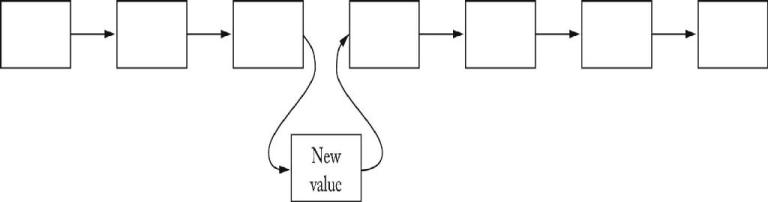
add adds element before iterator position remove removes element returned by last call to next
int[] numbers = new int[10]; 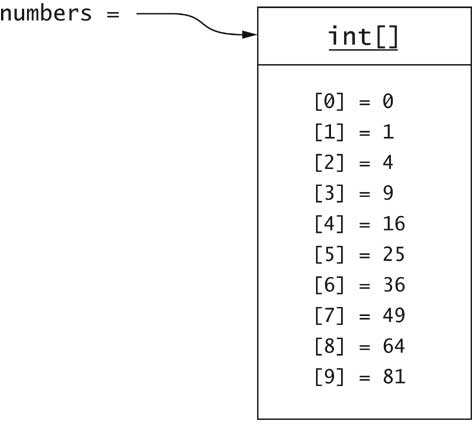
[] operator:
int n = numbers[i]; length member yields number of elements
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++)
for (int n : numbers) . . . null:
numbers = new int[0];
int[][] table = new int[10][20]; int t = table[i][j];
void main(String[] args)
args parameter of main is initialized with command-line arguments java GreeterTest Mars
args.length is 1
args[0] is "Mars" public class Greeter
{
. . .
private static Random generator;
}
public class Math
{
. . .
public static final double PI = 3.14159265358979323846;
}
Math.sqrt public static Greeter getRandomInstance()
{
if (generator.nextBoolean()) // note: generator is static field
return new Greeter("Mars");
else
return new Greeter("Venus");
}
Greeter g = Greeter.getRandomInstance();
name sayHello
Greeter ArrayList
PI MAX_VALUE
get/set prefixes:
String getName() void setName(String newValue)
is/set prefixes:
public boolean isPolite() public void setPolite(boolean newValue)
public String sayHello()
{
return "Hello, " + name + "!";
}
public String sayHello() {
return "Hello, " + name + "!";
}
public class Greeter
{
private String name;
public Greeter(String aName) { . . . }
. . .
}
public interface first private Good: if (x > Math.sqrt(y)) Bad: if(x>Math.sqrt (y))
Good: int[] numbers Bad: int numbers[]
Good: h = HASH_MULTIPLIER * h + val[off]; Bad: h = 31 * h + val[off];